Autobiography and Memoir are often used as synonyms but there is a large variation between them. But you can tell them apart and be certain you're using the correct phrase if you know certain fundamental differences. Understanding the differences will also help you decide what to study; for example, once you grab a book marked "memoir" or "autobiography," you must know what to expect.
Check out the Comparison Table
What is a Memoir?
Memoir is derived from the French word mémoire, which means “memory or recollection.” A memoir is the account of a human's life that an individual has documented. Those life experiences are frequently based on journals, possibly using the first-person perspective or by a distant relative or friend who has access to their journals.
There is a wide variety of memoirs, all composed of a personal portrait of the subject. They typically relate the experiences of someone who overcame hardships or problems in unusual ways. They may also include confessionals, in which the memoir describes the writer's version of events that may differ from other versions.
Key Elements of a Memoir
The most effective memoirs use various techniques to tell their narrative to the reader. The following are the key components of excellent memoirs -
A Theme
It's tricky to want to include an event-by-event tale that has happened over the years while composing a book about your life events. But every powerful story in a strong memoir must also serve to further the theme, and memoir work should be centered on a particular theme or learning experience. A strong memoir will always have a memorable theme and it often depends on questions like -
- What do you hope readers will learn from your memoir?
- What is the main lesson you wish to convey?
Hurdles
The main events of any memoir should be outlined after you've decided on a theme. Memoirists frequently recount the events at a particular point in their lives whenever they desire or want it (such as academic or career accomplishments). By describing the significant barriers that prevented them from attaining their objectives, memoir authors might make the writing transition easier.
Empathetic Rhythm
The best memoirs generate strong feelings from the audience. The ability to write in the first person perspective enables you to convey the emotional resonance of each experience in addition to your topic.
Additional Narratives
Writing memoirs entails exploring the layers of the real-life narrative and accurately and transparently highlighting those positive memories. This is why collecting interesting tales from various sources is just one of a memoir's fundamental components.
Interviewing your companions who were present growing up may be beneficial for your memoir. They might have a unique viewpoint on some incidents you can add to your work.
Individual Style
Writing memoirs gives you the ability to share a narrative from your experience, but it also provides you with the opportunity to express it uniquely. Your individual word choice enters the picture here. Your individuality and perspective should be present on every page.
Honesty
The uncompromising honesty of a memoir is one of its main attributes. Keep in mind that readers go into a memoir anticipating a real story. Audiences are wise people. If anything in your memoir doesn't feel quite right, readers may pick it up right away.
The interaction between the writer and the reader may be severely harmed if they believe that the incidents in the memoir are fictitious. You should therefore be prepared to communicate your tale openly and sincerely.
The Function of a Memoir
Firstly, an author has the chance to impart what they have discovered via their experiences and knowledge in a memoir. A memoir concentrates on specific facts related to the main theme rather than detailing every significant life experience. This strategy supports the writer in discovering significance and insight into their own lives.
Secondly, an author has the chance to impart their self-realizations and discoveries via the stated life events in a memoir. A memoir concentrates on specific facts related to the main theme rather than detailing every significant life experience. This strategy supports the writer in discovering significance and insight into their own lives.
What is Autobiography?
The first-person description of an individual's entire life is called an autobiography. Autobiographies' defining quality is their topic; they are frequently authored by famous people, including corporate leaders, politicians, athletes, and people in the media. A person's early success, status, wealth, or brilliance may be documented in an autobiography.
As they concentrate more on information, autobiographies are much more structured than memoirs. Autobiographies frequently recount events as they were, often using simple language and sequential storytelling. To verify their authenticity, details are reviewed before publication.
Key Elements of Autobiography
Life Description
Describe your life at the beginning. Start with the beginning of your journey and end around the moment you choose to compose your autobiography—all there is to it. Although it makes sense, to begin with your early life, you could wish to start by briefly reviewing your family heritage.
Your life biography might follow a timeline, although it is not required to list your years of existence in detail.
Philosophy of Life
Talks about life. You look into what life would mean to you and what it represents in the latter part of the exercise. Explain your outlook on life. The value of knowing who you are and where you are going. Describe your level of happiness in life. Tell them what you do for fun and how you keep yourself motivated.
The Vision of the Future
Your perspective on your destiny, how you picture your life unfolding, and a forecast about where your journey will go using your views. Decide if you can explain your perfect world in considerable detail or if you can think objectively. Then, see a meaningful and satisfying life before you. Everything depends on you.
Conclusion
Lastly, conclude succinctly. Write a summary of everything you've said. Describe your motivation for writing this autobiography in a few terms. Remind your audience of the author's goal and assess whether you successfully got your point through.
Finish your autobiography with something uplifting.
Function of Autobiography
Autobiographies give authors a clear line of communication with readers and future generations. The purpose of an autobiography is to impress its audience with something meaningful. Creating an autobiography allows the author to connect to readers and inspire them with motivating tales of personal successes, setbacks, and critical incidents. Life experiences enable people of various demographics and ages to interact with one another, bridging the generational gap.
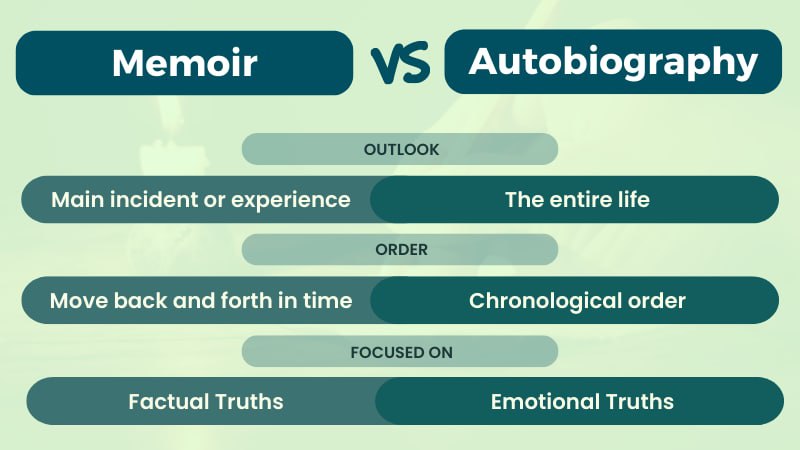
Key Differences Between Memoir & Autobiography
The key differences between them are described below-
Focus
Memoirs only focus on a specific period of the original story. Still, autobiographies typically include the writer's entire existence until the moment of writing.
Nature
Given they are renowned and significant personalities, authors frequently share their personal stories in autobiographies. Whether well-known or not, anyone can write a Memoir.
Readers
Readers like autobiographies to learn more about a specific (often famous) individual. They enjoy memoirs due to their drive to the author's tone or approach or simply because they are fascinated by a particular topic or event.
Order
Memoirs frequently jump between periods, but autobiographies are generally presented in chronological sequence.
Emphasis
A memoir highlights the author's knowledge and emotional depth, whereas an autobiography focuses more on the events and how the writer belongs to the historical evidence.
Practical Example:
The Year of Magical Thinking by Joan Didion (A Memoir)
Didion chronicles the initial year of her life just after the passing of her spouse, John Gregory Dunne, in The Year of Magical Thinking. Dunne passes out one night, and Didion's life is irrevocably altered. She spends the following year attempting to understand his death and negotiating the rough waters that are her sorrow. She gets by on the strength of her ideas, scientific and behavioral studies, and her own "magical thinking"—the delusion that her acts or ideas may alter the path of happenings.
The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin
One of the first presidents of the United States wrote a great deal (and I do mean a lot!) about events, lifestyle, and good judgment. His studies, quotations, and counsel are still employed today, and the $100 bill has his image. The wise words of Benjamin Franklin, like "We are all created uninformed, but one has to strive to remain foolish," continue to be used still. He is also the author of the proverb "Tell me and I forget," which is used in many institutions. His autobiography is chock-full of his exploits, worldview, and experience. His autobiography demonstrates how highly he cherished learning through examples (tales) about his ongoing efforts to grow and learn.
Memoir vs. Autobiography Comparison Table
Let’s look at the comparison table so that the differences between Memoir and Autobiography can be pinpointed precisely-
|
Basis of Comparison |
Memoir |
Autobiography |
|
What is it? |
A memoir is a literary form that records memories of a person's experiences throughout his or her life. |
The literary genre known as autobiography includes works in which writers recount or write about their own experiences. |
|
Covers |
a personal narrative of a particular moment or encounter |
a record of one's life |
|
Focuses on |
examining in-depth major occurrences or experiences in the memoirist's life. |
Everything that happened in the main character's life. |
|
Nature |
Subjective |
Detailed |
|
Key Components |
presents information in the person's own words. |
offers information based on the subject's personal experience. |
|
Reflect |
Written to consider and delve feeling of an encounter |
Written to educate and clarify the reasoning and ideas behind deeds and judgments |
|
Order |
Can begin anywhere. |
Chronologically organized. |
