Communication is the key to effective marketing; you must reach your target on appropriate channels at the right moment with proper messages.
Buyer personas and ideal customer profiles are two of the most popular ways marketers know about their customers. Before addressing when and how to use each, let's first take a closer look at what a buyer persona and an ideal customer profile are.
Check out the Comparison Table
What is the Buyer Persona?
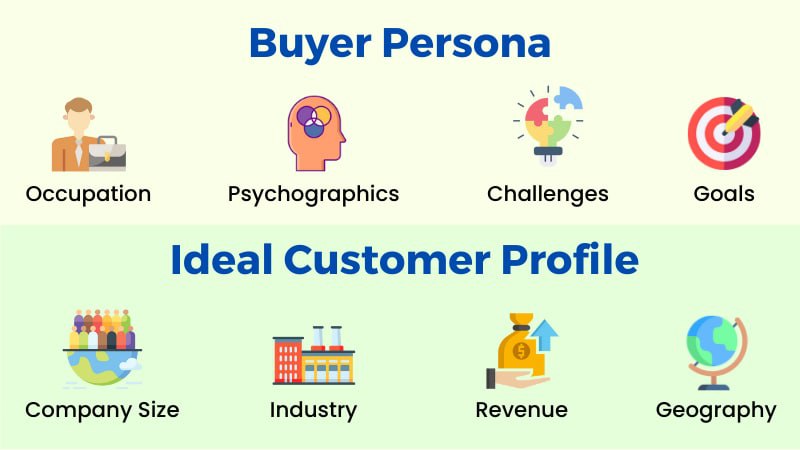
A buyer persona is a description of the desired audience based on findings. Buyer personas outline the characteristics of your ideal clients, including their daily routines, problems they encounter, and decision-making processes.
This forges a trustworthy relationship with your customers and encourages them to complete the purchase. With the guidance of buyer personas, you can better concentrate on discovering your customers' needs and expectations so that you may build and advertise their desired products.
Key Features of a Buyer Persona
A buyer persona is more distinctive and individual. Less importance is put on the negative traits of your financial entity and more on the unique stories of the customers.
Desires – What goals or objectives does each buyer persona have? This might apply to your personal or professional life.
Challenges – What prevents your buyer persona from attaining the above goals?
Outside interests – What do they enjoy doing while they're not working?
Communities – To which groups do they look for current affairs?
Importance of Buyer Persona
Buyer personas is crucial for market segmentation. They enable you to divide up your clientele into various segments. It improves your comprehension of your clients. You may more easily adapt your messaging, information, goods, and offerings to their unique requirements, behaviors, and worries as a result. Also-
- increase the number of the proper kind of consumers you can keep.
- Tools like buyer personas can help you interact with the buyers.
- You will become a productive and successful marketer with a buyer persona.
- User-driven design: You concentrate on the user's requirements.
- Understanding the many driving forces and purchase tendencies of your clients.
- Study on buyer personas will guarantee that your business speaks with your customers.
What is an Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)?
An ideal customer profile is a representation of a hypothetical client who would benefit significantly from your commodity and who would also significantly benefit your business. The kind of user that is the cheapest to acquire, has a high future value, is less prone to leave, and finally starts to promote your products.
Key Features of an Ideal Customer Profile
An ideal customer profile has a stronger quantitative component. Less attention is paid to the specific individuals you encounter, and more is paid to the firm's demography and quantifiable characteristics.
Industry – More general examples include judicial, medical, and educational fields. The further you can research in a field, the better.
Company Size – Branding a small firm with seven people and a company with thousands of workers are quite different things.
Department – Is the accounting department of the business a user of your good or service? Or would it make their salesmen more effective at what they do?
Job titles – This describes the particular kind of employee at the corporation you wish to work with. Although job descriptions are present in both types of identities, some marketers might opt to save information for their customer base.
Importance of Ideal Customer Profile
You could be thinking about whether you require an ICP now since you understand what it comprises. Most marketers believe that building, storing, and using customer profiles are an essential part of their business. The advantages listed below may have convinced these marketers to view ICPs as fundamental:
- Concentrate your sales efforts on the businesses that are most inclined to purchase from you.
- Offer your goods or services to businesses with the best chance of success. A user who isn't a great fit for your services consumes the work of your Customer Support team and can wind up eventually costing your business more than the relationship is worth.
- Make wise short lists of businesses to concentrate on, keep an eye out for buying indications inside these businesses, and move quickly whenever a sales opportunity comes up.
- Be extremely focused on your marketing efforts. When you are aware of your ideal customer profile, you can target your advertising and the audience for your content.
Key Differences Between Ideal Customer and Buyer Persona
All of those considerations, though, depend on having a clear grasp of the audience you're aiming to reach. You probably wouldn't be able to grab people's attention and build strong customer relationships if you do not even learn much about the individuals who wish to buy your goods or services. The key differences between Buyer Persona and an Ideal Customer Profile are listed below-
Basic Difference
An ICP and a Buyer's persona are fundamentally different from one another. An ideal customer profile is more quantitative while a buyer persona is more qualitative.
Definition
Your buyer persona is a thorough examination of the people who bought from you, but your ideal customer profile describes the kind of individuals or businesses you strive to sell to.
Purpose
A target market is generically described by ideal customer profiles, whereas buyer personas identify particular industry subsets.
Components
Both use numerical information, such as financial planners and pay, but an ICP is more centered on the figures. The core of ICPs are facts like firm size, personnel numbers, and similar information. A buyer persona is more qualitative and includes the goals, difficulties, and anxieties of the customer.
Best Suited Areas
ICPs perform nicely for the sales pipeline, whereas buyer personas offer more precise and realistic knowledge of the target demographic that your company is trying to reach.
Focus
While buyer personas are built on your potential leads, ideal customer profiles concentrate on your current consumers.
Practical Example
J & J is a healthcare company with several potential customers. Personas are about connecting with each distinctive group on a personal basis. Working moms were one of the main target demographics in this scenario.
"Working Mom Monica" would be one of the buyer personas as a result. They began with personal conversations, took the most important takeaways from those discussions, gathered the information, and then made her persona card.
J & J are also aware of Monica's internet usage as a research tool. They can use these hints to determine how to promote Monica most effectively. First, online marketing initiatives like email marketing or commercial media content should be implemented as they know that Monica frequently browses the web.
Second, starting a blog with articles on healthy lifestyles, like easy home treatments for common illnesses or family-friendly dishes, could be a terrific way to get to know Monica. They might even influence her to sign up for email notifications on stories. The main objective is to boost her level of pleasure and enhance the likelihood that she will choose one of their services.
J & J, on the other hand, seeks to create an ideal customer profile to assist them in determining a prospect's potential. J & J should probably invest more time into marketing a new opportunity if they exactly match their ideal customer profile. Although the selling process may be lengthy and the potential reward may be less for businesses that fit this image slightly worse, J & J should pursue them later and with much less time and energy.
Buyer Persona vs Ideal Customer Profile Comparison Table
Let’s take a look at the comparison table below so that the details and differences can be pinpointed precisely -
|
Basis of Comparison |
Ideal customer profile |
Buyer persona |
|
Use |
Used mainly by B2B companies |
Used by both B2B and B2C companies |
|
Purposes |
Find businesses that are a better match for the enterprise. |
Recognize the decision-makers and develop meaningful relationships with them. |
|
Focus |
Based on statistical data from CRM, analytics tools, and customer interviews |
Focuses on the individuals behind a purchase |
|
Key Components |
Company size, industry, geography, titles, special requirements |
ICPs, KPI, challenges, goals, professional background, buying behavior |
|
Stage of Pipeline |
Top lead generation |
All stages |